Difference between revisions of "Herman Potočnik Noordung and Vitanje"
(mwtool_article) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{{Infobox | {{Infobox | ||
| − | |name = | + | |name = Herman Potočnik Noordung and Vitanje |
| − | |street = | + | |local name = Herman Potočnik Noordung in Vitanje |
| − | |town = | + | |street = |
| + | |town = | ||
|telephone = | |telephone = | ||
|logo = Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje.jpg | |logo = Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje.jpg | ||
|map = http://www.openstreetmap.org/?lon=15.297&lat=46.3824&zoom=13&layer=mapnik | |map = http://www.openstreetmap.org/?lon=15.297&lat=46.3824&zoom=13&layer=mapnik | ||
| − | |website = http:// | + | |website = http://noordung.blogspot.si |
|contacts = {{contact | |contacts = {{contact | ||
| − | |name = | + | |name = |
| − | |email = | + | |email = |
| − | |telephone = | + | |telephone = |
|established by = Municipality of Vitanje | |established by = Municipality of Vitanje | ||
|map = | |map = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | | | + | |accounts = |
| + | https://www.facebook.com/HermanPotocnik | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
{{Teaser| | {{Teaser| | ||
| − | |||
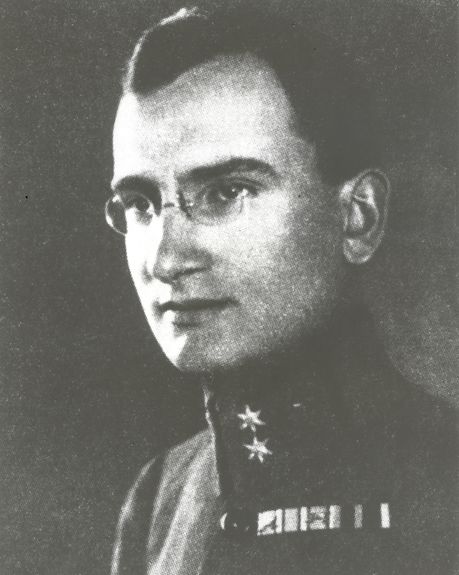
| − | + | [[Herman Potočnik Noordung]] (1892–1929) was a rocket engineer and a space flight pioneer and a visionary who conceived the idea of a geostationary satellite. | |
| − | The initiative of [[Dragan Živadinov]] ([[Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet]]) to put up a memorial centre that would showcase Potočnik's life and work was given a green light in the Municipality of Vitanje, a small town (today circa | + | The initiative of [[Dragan Živadinov]] ([[Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet]]) to put up a memorial centre that would showcase Potočnik's life and work was given a green light in the [[Municipality of Vitanje]], a small town (today circa 880 inhabitants). |
| − | + | In December [[Established::2006]], in advance of the 115th anniversary celebrations of Potočnik's birth the Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre was opened at Grajski trg 1, in the house where Herman's grandfather worked. In 2012, a [[Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT)]] was opened in Vitanje. The KSEVT team represented Slovenia at the 2014 Architecture Biennale in Venice with The Problem of Space Travel – Supre:architecture project, which delved into the fundamentals of architecture through the opus of the pioneer of space architecture. | |
}} | }} | ||
==Herman Potočnik Noordung== | ==Herman Potočnik Noordung== | ||
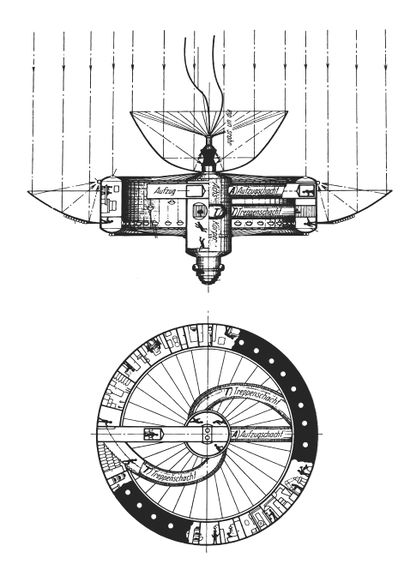
| − | A visionary with an extraordinary technological imagination and an astounding philosophy of existence, [[Herman Potočnik Noordung]] was the author of the first strategic plan for the human exploration of space, whose predictions enjoy growing confirmation with each new extra-terrestrial accomplishment in the modern era | + | A visionary with an extraordinary technological imagination and an astounding philosophy of existence, [[Herman Potočnik Noordung]] was the author of the first strategic plan for the human exploration of space, whose predictions enjoy growing confirmation with each new extra-terrestrial accomplishment in the modern era. |
| − | == | + | Born in 1892 to Slovene parents in Pula, Croatia, he spent World War I as a first lieutenant, assisting in the construction of railway lines and bridges on the Soča and Piava rivers. In 1925 he completed his engineering and electro-technical studies in Vienna with the title Specialist in Rocket Technology. |
| + | |||
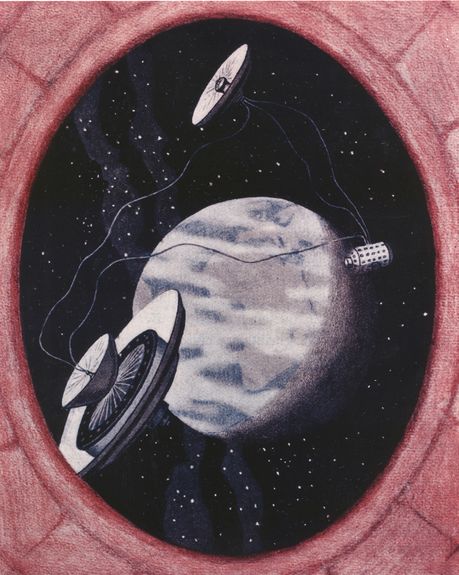
| + | Years of dire economic hardship and illness coincided with his design of a futuristic rocket and his exploration of space-travel technology. Despite setbacks the first notes for a book emerged, inspired by the writings of German rocket scientist Hermann Oberth. By 1928 Noordung had completed a rough draft of all the chapters, and in 1929, shortly before his death, the book ''Das Problem der Befahrung des Weltraums'' was published. Running 188 pages and featuring 100 of his own drawings, it discusses gravity and ways of overcoming it, looks at space technology used in everyday life, contemplates the efficiency of the rocket while warning against its possible misuse for military purposes, and envisions a geostationary satellite that would orbit the globe indefinitely with enviable precision. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The concluding thought of the fourth and last segment of Potočnik's book is about the drive for nuclear and photonic technology which would make it possible to travel to nearby planets in our universe. The book considers space travel not as mere day-dreaming but as a very real technological possibility. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre 2006–2015 == | ||
The Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre was a one-artefact-museum – [[Herman Potočnik Noordung|Herman Potočnik Noordung's]] book ''The Problem of Space Travel'' (1929). The memorial room slightly resembled the interior of a space observatory. Due to lack of physical memorabilia about his life, the interior of an observatory capsule presented videos with statements of renowned historians, cosmonauts and astronauts for instance: Tatjana Nikolajevna Zhelnina, Pavel Klushantsev, Jurij Baturin, Roger Launius, Frederick I. Ordway III, and sir Arthur C. Clarke. Clarke introduced Potočnik's design of the wheel space station to Stanley Kubrick who used it (uncredited) in the film ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (1969). | The Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre was a one-artefact-museum – [[Herman Potočnik Noordung|Herman Potočnik Noordung's]] book ''The Problem of Space Travel'' (1929). The memorial room slightly resembled the interior of a space observatory. Due to lack of physical memorabilia about his life, the interior of an observatory capsule presented videos with statements of renowned historians, cosmonauts and astronauts for instance: Tatjana Nikolajevna Zhelnina, Pavel Klushantsev, Jurij Baturin, Roger Launius, Frederick I. Ordway III, and sir Arthur C. Clarke. Clarke introduced Potočnik's design of the wheel space station to Stanley Kubrick who used it (uncredited) in the film ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' (1969). | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | {{Image|Photo Edi Einspieler (60).jpg}} | ||
| + | |||
The programme of the Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje was closely linked to the artistic endeavours of the [[Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet]] and developed by [[Dragan Živadinov]] (Merger of Art and Science), [[Dunja Zupančič]] (Postgravity Art) and [[Miha Turšič]] (Culturalisation of Space). | The programme of the Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje was closely linked to the artistic endeavours of the [[Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet]] and developed by [[Dragan Živadinov]] (Merger of Art and Science), [[Dunja Zupančič]] (Postgravity Art) and [[Miha Turšič]] (Culturalisation of Space). | ||
| Line 47: | Line 56: | ||
{{YouTube|mb629By_qQU}} | {{YouTube|mb629By_qQU}} | ||
Cosmonaut Jurij Baturin speaks on the opening of his exhibition ''Meeting With Earth'' (2009) | Cosmonaut Jurij Baturin speaks on the opening of his exhibition ''Meeting With Earth'' (2009) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT) == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT)]] opened in Vitanje in September 2012. The building design is the work of four architectural bureaus which established the Architectural Union for Vitanje (AZZV): [[Bevk Perović Arhitekti]], [[Dekleva Gregorič Arhitekti]], [[Ofis Arhitekti]], and [[SADAR + VUGA Architects]]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 67: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * [http:// | + | * [http://noordung.blogspot.si/ KSEVT projects since 2007] |
* [http://noordung.vesolje.net/vsebina/index.htm Herman Potočnik Noordung] on Vesolje.net website | * [http://noordung.vesolje.net/vsebina/index.htm Herman Potočnik Noordung] on Vesolje.net website | ||
* [http://noordung.blogspot.com Herman Potočnik Noordung blog] | * [http://noordung.blogspot.com Herman Potočnik Noordung blog] | ||
| Line 63: | Line 76: | ||
{{Gallery}} | {{Gallery}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:New media art event organisers]] | ||
| + | [[Category:New_media_art_festival_and_event_organisers]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:33, 19 February 2021
-
25 Feb 2016
The opening of the Herman Potočnik Noordung memorial room, organised in cooperation with the Embassy of the Republic of Slovenia Moscow,
-
to
1 May 2010
31 Oct 2010
Slovene Pavillion at Expo 2010 Shanghai featuring Herman Potočnik Noordung, Starck with Riko, Primož Trubar and World Book Capital Ljubljana 2010, with contributions by Oskar Kogoj, Matej Andraž Vogrinčič, and Slavoj Žižek
Herman Potočnik Noordung
A visionary with an extraordinary technological imagination and an astounding philosophy of existence, Herman Potočnik Noordung was the author of the first strategic plan for the human exploration of space, whose predictions enjoy growing confirmation with each new extra-terrestrial accomplishment in the modern era.
Born in 1892 to Slovene parents in Pula, Croatia, he spent World War I as a first lieutenant, assisting in the construction of railway lines and bridges on the Soča and Piava rivers. In 1925 he completed his engineering and electro-technical studies in Vienna with the title Specialist in Rocket Technology.
Years of dire economic hardship and illness coincided with his design of a futuristic rocket and his exploration of space-travel technology. Despite setbacks the first notes for a book emerged, inspired by the writings of German rocket scientist Hermann Oberth. By 1928 Noordung had completed a rough draft of all the chapters, and in 1929, shortly before his death, the book Das Problem der Befahrung des Weltraums was published. Running 188 pages and featuring 100 of his own drawings, it discusses gravity and ways of overcoming it, looks at space technology used in everyday life, contemplates the efficiency of the rocket while warning against its possible misuse for military purposes, and envisions a geostationary satellite that would orbit the globe indefinitely with enviable precision.
The concluding thought of the fourth and last segment of Potočnik's book is about the drive for nuclear and photonic technology which would make it possible to travel to nearby planets in our universe. The book considers space travel not as mere day-dreaming but as a very real technological possibility.
Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre 2006–2015
The Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre was a one-artefact-museum – Herman Potočnik Noordung's book The Problem of Space Travel (1929). The memorial room slightly resembled the interior of a space observatory. Due to lack of physical memorabilia about his life, the interior of an observatory capsule presented videos with statements of renowned historians, cosmonauts and astronauts for instance: Tatjana Nikolajevna Zhelnina, Pavel Klushantsev, Jurij Baturin, Roger Launius, Frederick I. Ordway III, and sir Arthur C. Clarke. Clarke introduced Potočnik's design of the wheel space station to Stanley Kubrick who used it (uncredited) in the film 2001: A Space Odyssey (1969).
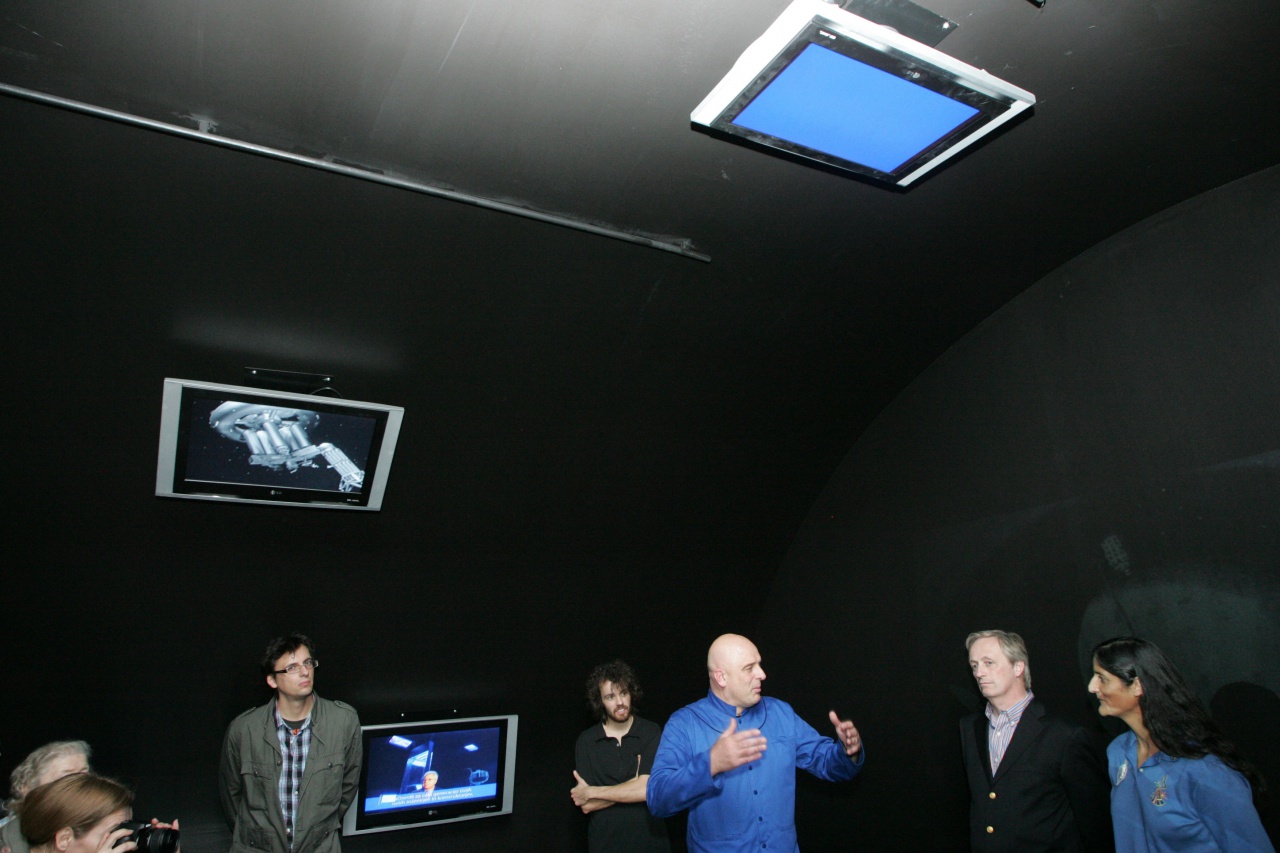 Sunita Williams visiting the Herman PotoÄnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje, 2009
Sunita Williams visiting the Herman PotoÄnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje, 2009
The programme of the Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje was closely linked to the artistic endeavours of the Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet and developed by Dragan Živadinov (Merger of Art and Science), Dunja Zupančič (Postgravity Art) and Miha Turšič (Culturalisation of Space).
The memorial centre occasionally hosted astronauts (for example, Christer Fuglesang, Sunita Williams) and other prominent guests. In May and June 2009 the Herman Potočnik Noordung Memorial Centre Vitanje hosted an exhibition of Russian scientist and cosmonaut Jurij Baturin with the title Meeting with Earth.
Cosmonaut Jurij Baturin speaks on the opening of his exhibition Meeting With Earth (2009)
Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT)
The Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT) opened in Vitanje in September 2012. The building design is the work of four architectural bureaus which established the Architectural Union for Vitanje (AZZV): Bevk Perović Arhitekti, Dekleva Gregorič Arhitekti, Ofis Arhitekti, and SADAR + VUGA Architects.
See also
- Cultural Centre of European Space Technologies (KSEVT)
- Noordung Cosmokinetic Cabinet
- Delak Institute
External links
- KSEVT projects since 2007
- Herman Potočnik Noordung on Vesolje.net website
- Herman Potočnik Noordung blog
- Herman Potočnik on Wikipedia
- Potočnik's book The Problem of Space Travel. The Rocket Motor, The NASA History Series online (no illustrations) and on Google Books
- Municipality of Vitanje website presentation (in Slovenian)
- The KSEVT project presentation, Bevk Perović Arhitekti